Cisco ACI Deployment Models
Cisco ACI Deployment Models
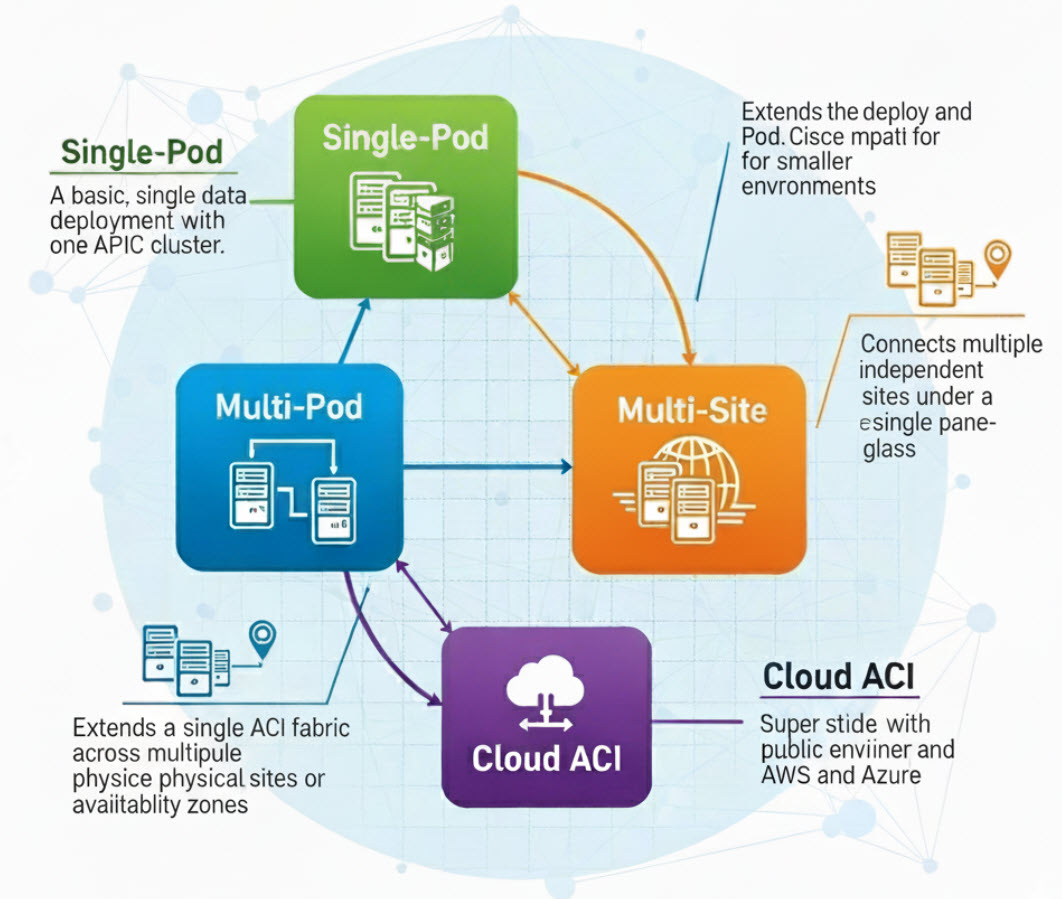
Understanding the Difference: Single-Pod, Multi-Pod, Multi-Site, and Cloud ACI
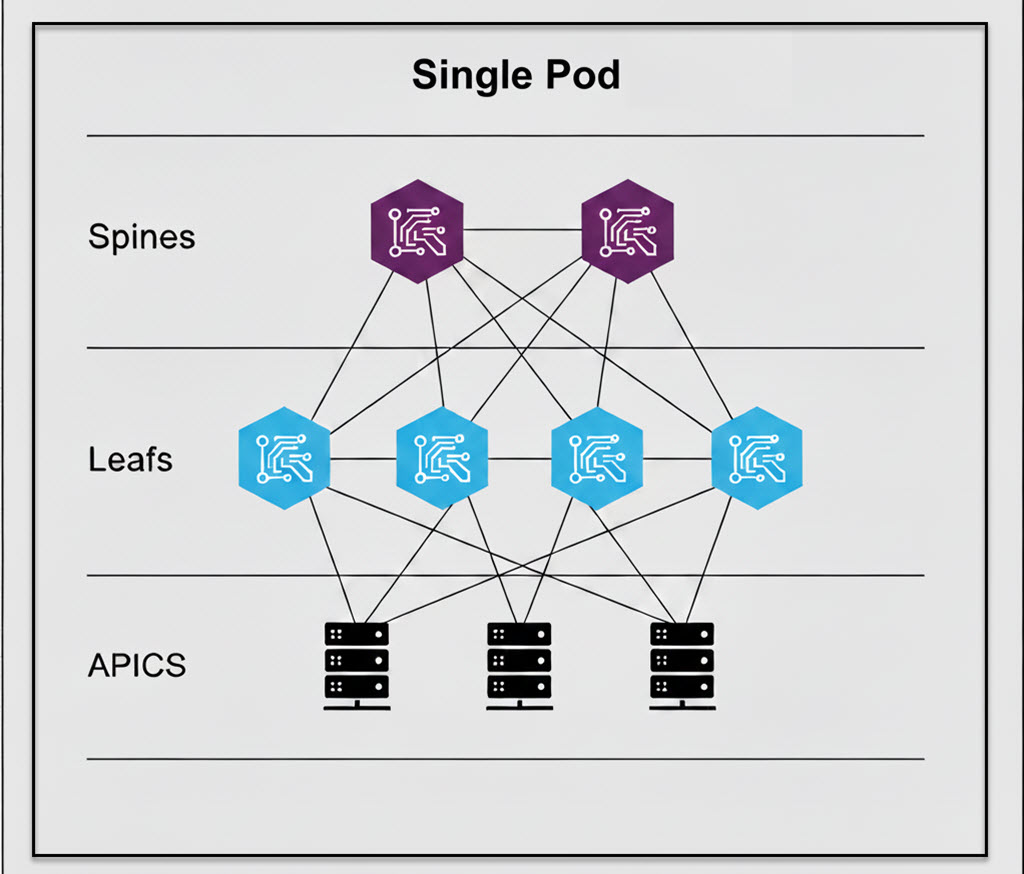
Standalone Single-Pod
Architecture
A single-pod deployment consists of a single ACI fabric, managed by a single Application Policy Infrastructure Controller (APIC) cluster. It's a self-contained environment, typically housed within a single data center.
Management
Management is centralized through the single APIC cluster. All policies, configurations, and monitoring are handled from this single point of control.
Use Cases
- Small to medium-sized data centers.
- Single-site deployments.
- Environments where low latency is critical.
Multi-Pod Deployment
Architecture
Multi-pod extends the ACI fabric across multiple physical locations or "pods." These pods are interconnected via an Inter-Pod Network (IPN) but are all managed by a single, stretched APIC cluster.
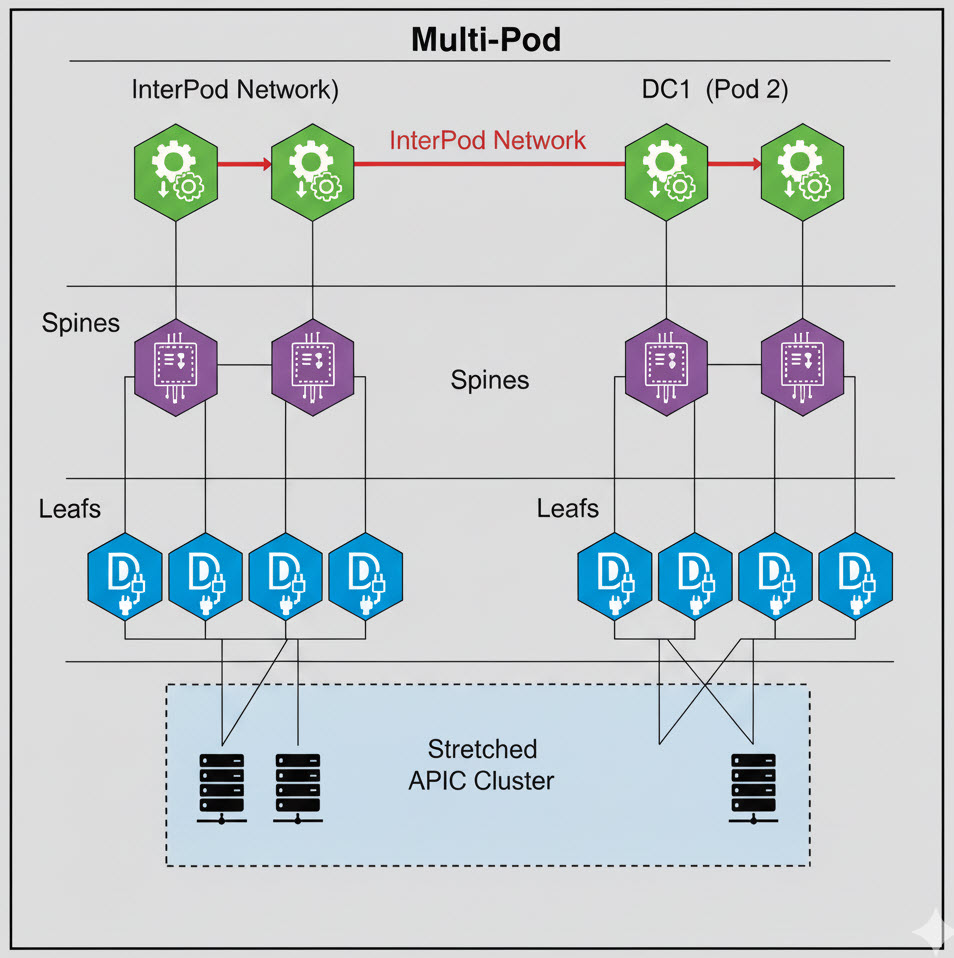
Management
Similar to single-pod, multi-pod is managed by a single APIC cluster. This provides a unified management plane across all pods, simplifying administration of a distributed environment.
Use Cases
- Large enterprises with multiple data centers in the same metro area.
- Disaster recovery solutions with lower latency requirements.
- Scaling a single ACI fabric beyond the limits of a single pod.
Multi-Site Deployment
Architecture
Multi-site connects two or more independent ACI fabrics, each with its own APIC cluster. The Cisco Multi-Site Orchestrator (MSO) is used to manage policies and connectivity between these distinct sites, which are true separate availability zones.
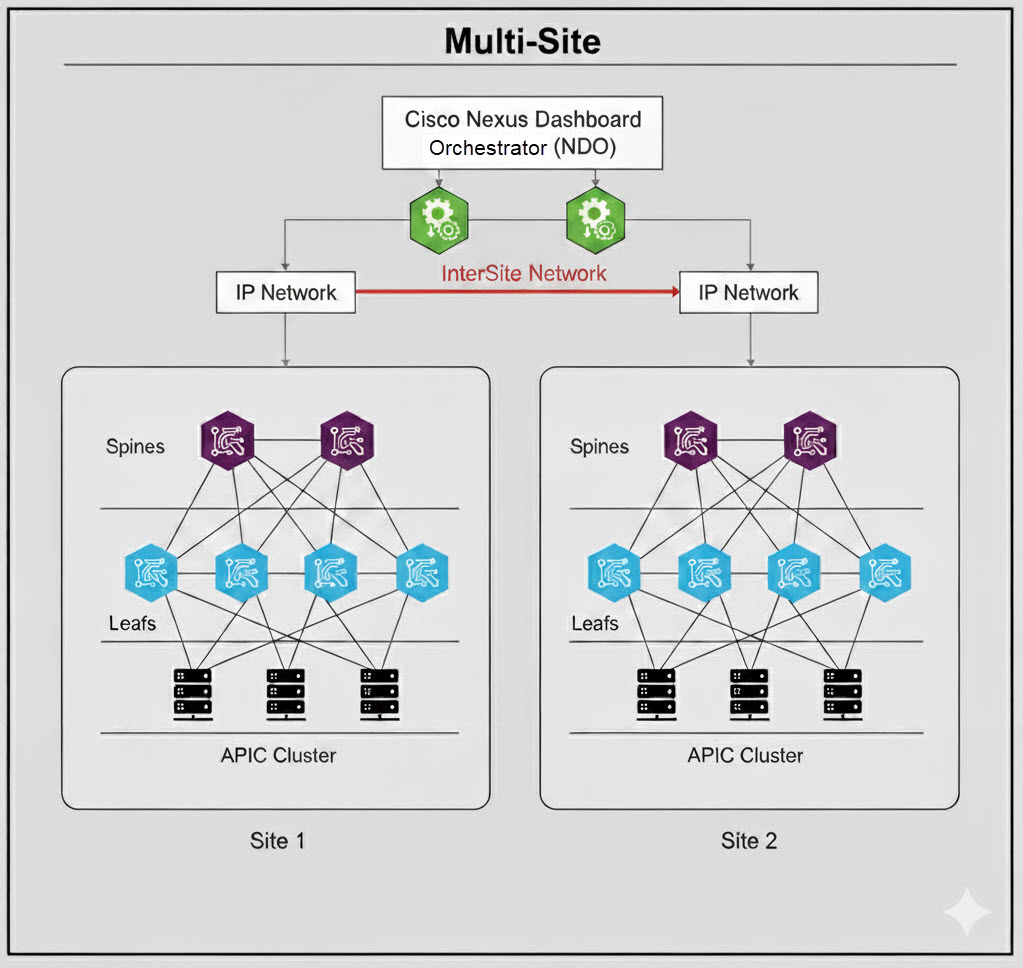
Management
Provides a federated management model. The MSO manages inter-site policies, while each site's APIC cluster manages local fabric policies. This allows for both centralized governance and local autonomy.
Use Cases
- Geographically dispersed data centers (inter-continental).
- High-level disaster recovery and business continuity.
- Separating failure domains for maximum application resilience.
Cloud ACI Deployment
Architecture
Cloud ACI extends the ACI policy model into public cloud environments like AWS and Microsoft Azure. It uses a Cloud APIC instance running in the public cloud to translate ACI policies into the cloud provider's native constructs.
Management
Achieves consistent network and security policy management across on-premises data centers and public clouds. The on-prem APIC or MSO can communicate with the Cloud APIC for a unified hybrid or multi-cloud strategy.
Use Cases
- Hybrid cloud deployments.
- Seamless application migration to the cloud.
- Consistent security and governance across all environments.
Key Differences at a Glance
| Feature | Single-Pod | Multi-Pod | Multi-Site | Cloud ACI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scope | Single location | Metro area | Geographically dispersed | On-prem to public cloud |
| Management | Single APIC cluster | Single APIC cluster | MSO + local APICs | APIC/MSO + Cloud APIC |
| Failure Domain | Single fabric | Per pod | Per site (independent) | Hybrid (on-prem/cloud) |
| Latency | Lowest | Low (sub-50ms RTT) | High latency tolerant | Variable (cloud network) |